Preventing Gingivitis: Protect Your Gums and Teeth
Gingivitis causes gum inflammation and bleeding, increasing the risk of tooth loss and gum disease. Plaque buildup along the gumline triggers gingivitis by irritating gum tissue. Poor oral hygiene, smoking, and health conditions increase the risk of developing gingivitis. Early signs include red, swollen, and bleeding gums while brushing or flossing. Treating gingivitis early prevents it from progressing to periodontitis, which damages bone and tooth stability. Brushing, flossing, and regular dental checkups reduce plaque and improve gum health. Proper oral care strengthens gum attachment and reduces sensitivity. Understanding how to prevent gingivitis helps protect long-term dental health. Let’s explore effective strategies to stop gingivitis before it starts.
Brush and Floss Daily to Remove Plaque
Brushing and flossing daily prevent plaque buildup and gum inflammation. Plaque forms when food particles mix with bacteria in the mouth. If not removed, plaque hardens into tartar, which irritates the gums. Brush twice a day using a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Clean along the gumline using gentle, circular motions to remove plaque. Floss daily to clean between teeth and under the gumline. Antibacterial mouthwash reduces bacteria and freshens breath. Regular plaque removal reduces gum inflammation and improves tooth strength. Consistent brushing and flossing protect against cavities and gum disease. Clean teeth and gums increase overall comfort and confidence.
Schedule Regular Dental Checkups
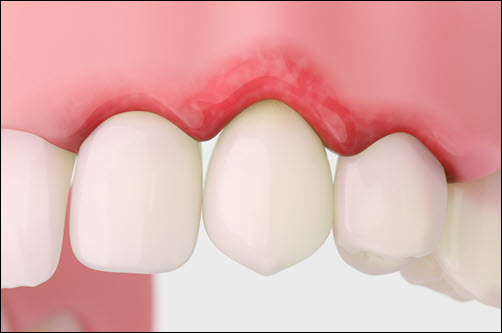 Professional cleanings remove plaque and tartar that brushing and flossing miss. Dentists use specialized tools to clean beneath the gumline and reduce inflammation. Regular dental exams allow early detection of gingivitis before it worsens. Dentists check gum pocket depth and measure gum health during checkups. Early detection and treatment prevent gingivitis from progressing to periodontitis. Fluoride treatments strengthen enamel and reduce sensitivity. Dentists may recommend deep cleaning (scaling and root planing) for early gum disease. Clean gums improve tooth attachment and reduce inflammation. Professional cleanings every six months maintain healthy gums and teeth. Regular dental visits protect long-term gum health and smile strength.
Professional cleanings remove plaque and tartar that brushing and flossing miss. Dentists use specialized tools to clean beneath the gumline and reduce inflammation. Regular dental exams allow early detection of gingivitis before it worsens. Dentists check gum pocket depth and measure gum health during checkups. Early detection and treatment prevent gingivitis from progressing to periodontitis. Fluoride treatments strengthen enamel and reduce sensitivity. Dentists may recommend deep cleaning (scaling and root planing) for early gum disease. Clean gums improve tooth attachment and reduce inflammation. Professional cleanings every six months maintain healthy gums and teeth. Regular dental visits protect long-term gum health and smile strength.
Eat a Healthy Diet to Strengthen Gums
A balanced diet improves gum health and supports overall dental strength. Foods rich in vitamins C and D strengthen gum tissue and improve immune response. Leafy greens, citrus fruits, and dairy products supply calcium and nutrients that strengthen gums and teeth. Crunchy fruits and vegetables like apples and carrots naturally clean teeth and stimulate saliva production. Avoid sugary snacks and acidic drinks, which increase plaque formation and gum irritation. Drinking water throughout the day flushes out food particles and bacteria. Better nutrition improves gum strength and reduces inflammation. Stronger gums improve overall tooth stability and bite strength. A healthy diet supports long-term dental and overall health.
Avoid Smoking and Tobacco Use
Smoking weakens gums and increases the risk of gingivitis and gum disease. Nicotine reduces blood flow to the gums, slowing healing and increasing inflammation. Tobacco products increase plaque buildup and deepen gum pockets. Smokers have a higher risk of gum recession and tooth loss. Quitting smoking improves blood circulation and gum attachment. Better gum health reduces sensitivity and improves tooth stability. Avoiding tobacco reduces staining and improves breath freshness. Improved gum strength increases overall dental comfort and bite function. Reduced inflammation decreases the risk of tooth loss and bone damage. Healthier gums support better long-term dental health and smile strength.
Use an Antibacterial Mouthwash
Antibacterial mouthwash reduces plaque and gum inflammation. Rinsing daily removes bacteria from hard-to-reach areas. Mouthwash reduces gum swelling and improves breath freshness. Alcohol-free mouthwash prevents dry mouth and reduces gum irritation. Antiseptic mouthwash kills bacteria and reduces the risk of gum infections. Dentists recommend mouthwash with fluoride to strengthen enamel and protect against decay. Swishing for 30 seconds improves plaque removal and gum health. Regular mouthwash use supports brushing and flossing, improving overall oral health. Better plaque control reduces gum sensitivity and bleeding. Consistent mouthwash use strengthens gum tissue and protects against gingivitis. Fresh breath increases comfort and confidence.
Protect Gums from Grinding and Clenching
Teeth grinding (bruxism) increases gum irritation and inflammation. Grinding places pressure on the gums and weakens tooth attachment. Wearing a custom night guard reduces grinding pressure and protects teeth and gums. Stress management techniques like deep breathing and meditation reduce jaw tension. Better sleep quality reduces muscle activity and grinding frequency. Reducing caffeine and alcohol intake lowers grinding risk and gum strain. Improved bite alignment reduces gum sensitivity and improves chewing strength. Protecting teeth from grinding prevents gum recession and inflammation. Stronger gum attachment increases tooth stability and bite comfort. Reduced pressure supports better long-term gum health.
Stay Hydrated to Improve Saliva Production
Saliva protects gums by washing away plaque and bacteria. Dehydration reduces saliva flow, increasing plaque buildup and gum irritation. Drinking water throughout the day improves saliva production and oral moisture. Chewing sugar-free gum stimulates saliva flow and reduces dry mouth. Saliva neutralizes acids and strengthens enamel. Hydrated gums reduce sensitivity and inflammation. Proper hydration improves chewing comfort and protects against cavities. Avoiding sugary and acidic drinks reduces plaque and protects gum tissue. Staying hydrated increases gum strength and reduces the risk of gingivitis. Better oral moisture supports long-term gum and tooth health.
Preventing gingivitis requires consistent oral care and proper hygiene. Brushing, flossing, and using mouthwash reduce plaque and strengthen gum health. Regular dental checkups allow early detection and treatment of gum inflammation. A balanced diet and proper hydration improve gum strength and reduce sensitivity. Quitting smoking improves gum circulation and reduces plaque buildup. Wearing a night guard and managing stress protects gums from grinding damage. Proper gum care reduces inflammation and increases tooth stability. Investing in gum health prevents gingivitis and improves overall dental comfort. Stronger gums and healthier teeth create a confident, balanced smile.

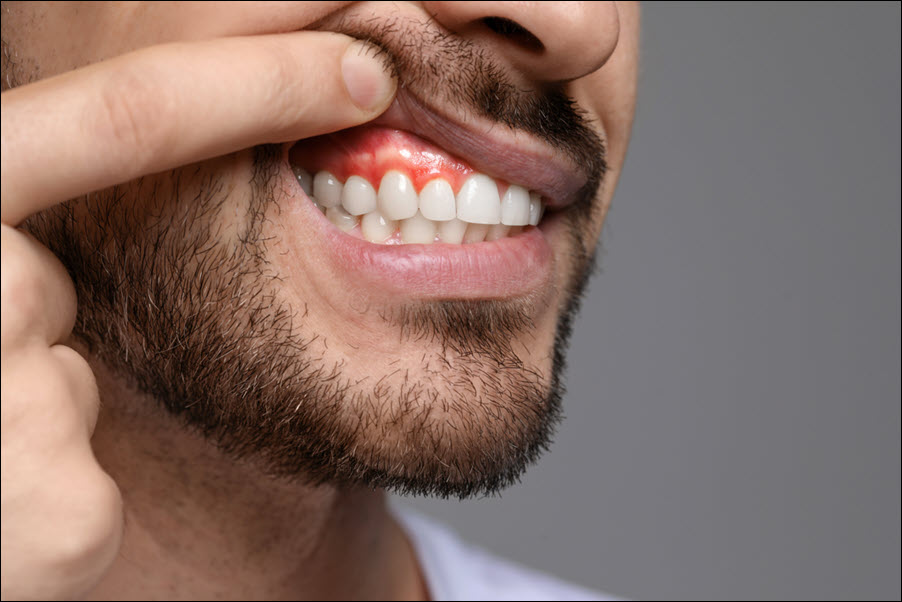

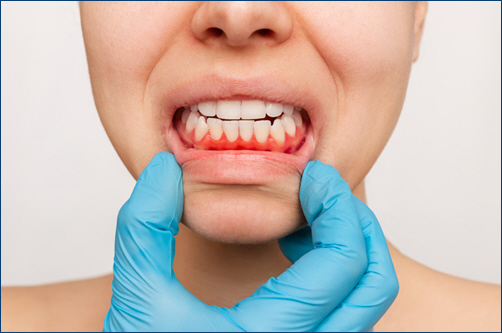 Regular Dental Checkups
Regular Dental Checkups